Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, energy production, and bone health. For growing children, ensuring adequate magnesium intake is crucial for their overall development and well-being. Incorporating magnesium into a child's diet is important for supporting development, improving sleep, and regulating mood. However, it can be challenging to determine if your child is getting enough magnesium or if they are deficient in this vital nutrient.
In this article, we will explore how to recognize the signs of magnesium deficiency in children, how much magnesium they need, and the best ways to incorporate magnesium-rich foods into their diet. We'll also touch on when magnesium supplementation may be necessary.
What is Magnesium, and Why is It Important for Children?
Magnesium is involved in over 300 chemical reactions in the body. It helps regulate muscle contraction, supports nerve function, and contributes to the production of energy at the cellular level. Calcium promotes muscle contraction while magnesium aids in muscle relaxation. Magnesium plays a significant role in children's growth, immune system function, and bone development.
Without enough magnesium, children may experience symptoms that affect their physical and mental health. It is important to maintain sufficient magnesium levels through a balanced diet.
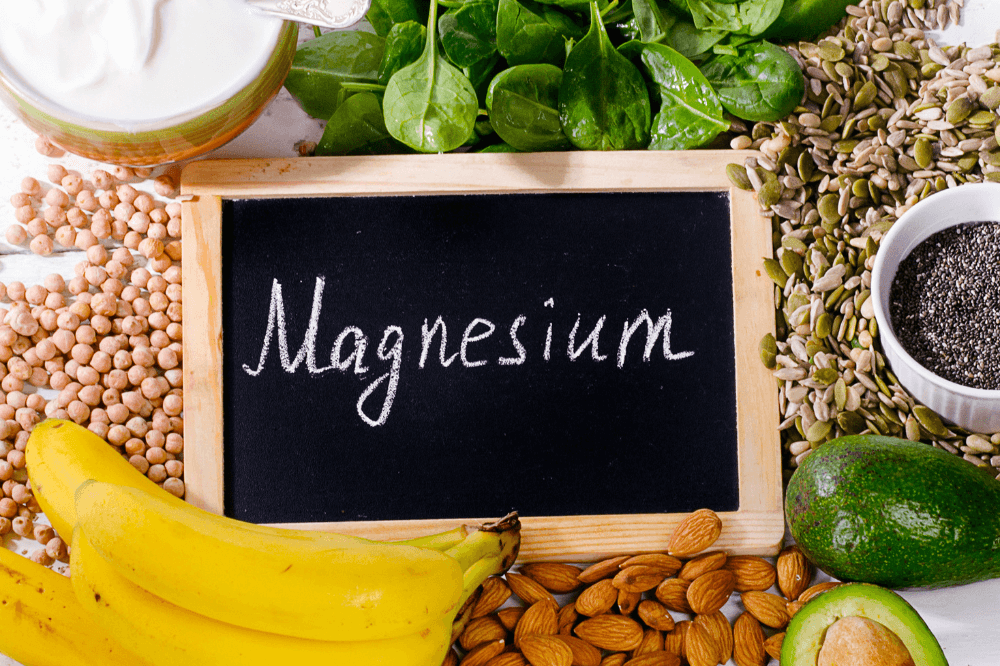
Signs of Magnesium Deficiency in Children
Magnesium deficiency symptoms in children can manifest in various ways, affecting both physical and mental health. While it's rare to have a severe deficiency, even a slight shortage can lead to noticeable symptoms. Here are some common signs of magnesium deficiency to watch out for:
- Muscle cramps and spasms: Magnesium helps muscles relax after contraction. Low levels can lead to cramps, spasms, and even growing pains.
- Fatigue and low energy: Magnesium is essential for energy production, and children with low magnesium may feel unusually tired or have low energy levels.
- Difficulty concentrating: A lack of magnesium can affect cognitive function, making it harder for children to focus and concentrate, especially during school.
- Mood swings and increased anxiety: Magnesium plays a role in regulating the body's stress response, and low levels can contribute to anxiety, irritability, or mood swings.
- Poor sleep: Magnesium promotes relaxation and can help children get a good night's sleep. Children with low magnesium may have trouble falling or staying asleep.
- Frequent headaches: Headaches, especially if accompanied by muscle tension, may be a sign of magnesium deficiency.
- Irregular heartbeat: In severe cases, magnesium deficiency can cause an irregular heartbeat or palpitations.
If your child exhibits any of these symptoms, it may be worth exploring their magnesium intake and consulting with a healthcare provider.
Causes of Magnesium Deficiency in Children
Several factors can contribute to magnesium deficiency in children. Some of the most common include:
- Poor diet: Children who consume a diet high in processed foods and refined carbohydrates may not be getting enough magnesium-rich foods. This is particularly common in picky eaters.
- Digestive disorders: Conditions such as celiac disease, which affect nutrient absorption, can deplete magnesium levels in the body.
- Chronic diarrhea: Digestive issues leading to diarrhea can cause children to lose magnesium rapidly.
- Increased stress: Stressful environments or situations may increase the body's demand for magnesium, leading to a deficiency if not adequately supplied.
The Link Between Magnesium Deficiency and Behavior
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to various behavioral issues in children, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, and depression. Research suggests that magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for mood regulation and focus.

When children don't get enough magnesium, it can affect their brain chemistry and lead to behavioral changes. For instance, low magnesium levels can contribute to increased irritability, difficulty concentrating, and hyperactivity. These symptoms are often seen in children with ADHD, making it important to consider magnesium levels when addressing behavioral concerns.
Parents may notice that their child is more anxious or has frequent mood swings. In such cases, evaluating their magnesium intake could be beneficial. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your child's diet, such as leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, can help support their mental health and improve their behavior. If dietary changes are not enough, consulting a healthcare provider about magnesium supplementation might be necessary.
By ensuring your child gets enough magnesium, you can help support their emotional well-being and cognitive function, potentially reducing the severity of behavioral issues.
How Much Magnesium Does Your Child Need?
The amount of magnesium a child needs depends on their age. According to health professionals, here are the recommended daily magnesium intake levels for children:
- 1–3 years: 80 mg of magnesium per day
- 4–8 years: 130 mg of magnesium per day
- 9–13 years: 240 mg of magnesium per day
- 14–18 years (boys): 410 mg of magnesium per day
- 14–18 years (girls): 360 mg of magnesium per day
It's important to ensure that your child meets these magnesium requirements through their diet to prevent potential deficiencies. Dietary supplements can help achieve the appropriate daily intake levels recommended by health authorities.
Best Sources of Magnesium for Children
Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your child's diet is the best way to ensure they are getting enough of this important mineral. Some of the best sources of magnesium include:
- Dark leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of magnesium.
- Pumpkin seeds: Roasted pumpkin seeds are not only tasty but also provide a good amount of magnesium.
- Chia seeds and flaxseeds: These seeds are packed with magnesium and can be easily added to smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal.
- Brazil nuts and almonds: Nuts like Brazil nuts and almonds contain high levels of magnesium and make for a healthy snack.
- Whole grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread offer magnesium along with other essential nutrients.
- Black beans and kidney beans: Legumes are great sources of magnesium and are easy to include in a variety of dishes.
- Dark chocolate: In moderation, dark chocolate can be a delicious way to increase magnesium intake.
A diet high in these magnesium-rich foods can help prevent childhood magnesium deficiencies and support overall health.

When Should You Consider Magnesium Supplementation?
If your child has a poor diet, suffers from a digestive disorder like celiac disease, or consistently shows signs of magnesium deficiency, magnesium supplements may be a good idea. However, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider before giving your child any supplements.
Magnesium supplements come in various forms, including magnesium oxide, magnesium citrate, and magnesium chloride. Your healthcare provider can recommend the best option based on your child's needs.
Can a Child Have Too Much Magnesium?
While magnesium is important, too much magnesium can lead to adverse side effects, especially when taken in supplement form. Symptoms of excess magnesium include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Low blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeat
High doses of magnesium, particularly from supplements, can be harmful, so it's crucial to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare provider if you're considering supplements.
Magnesium and Vitamin D: A Crucial Relationship
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption, which, in turn, is linked to magnesium levels. Adequate magnesium helps activate vitamin D in the body, which is essential for bone health. Without enough magnesium, the body may not utilize vitamin D efficiently, further impacting your child's health.
Stress and Magnesium Levels
Magnesium is known to play a role in the body's stress response. If your child is experiencing stress, their magnesium levels may deplete faster. Magnesium helps to calm the nervous system and can reduce the physical symptoms of stress, such as muscle tension and increased anxiety. Ensuring your child has enough magnesium can support their mental health and overall well-being.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
If you're concerned about your child's magnesium levels or suspect they may be deficient, it's important to consult a healthcare provider. They may recommend a blood test to check your child's magnesium levels and determine whether dietary changes or supplementation are necessary.
Conclusion
Magnesium is a crucial mineral for children's growth and development. From supporting muscle and nerve function to promoting healthy bones and a robust immune system, magnesium plays an essential role in your child's health. By incorporating magnesium-rich foods into their diet and monitoring their intake, you can help prevent magnesium deficiency and ensure they get the nutrients they need to thrive.
If you suspect your child is deficient in magnesium, consult a healthcare provider for guidance on proper magnesium intake and supplementation.